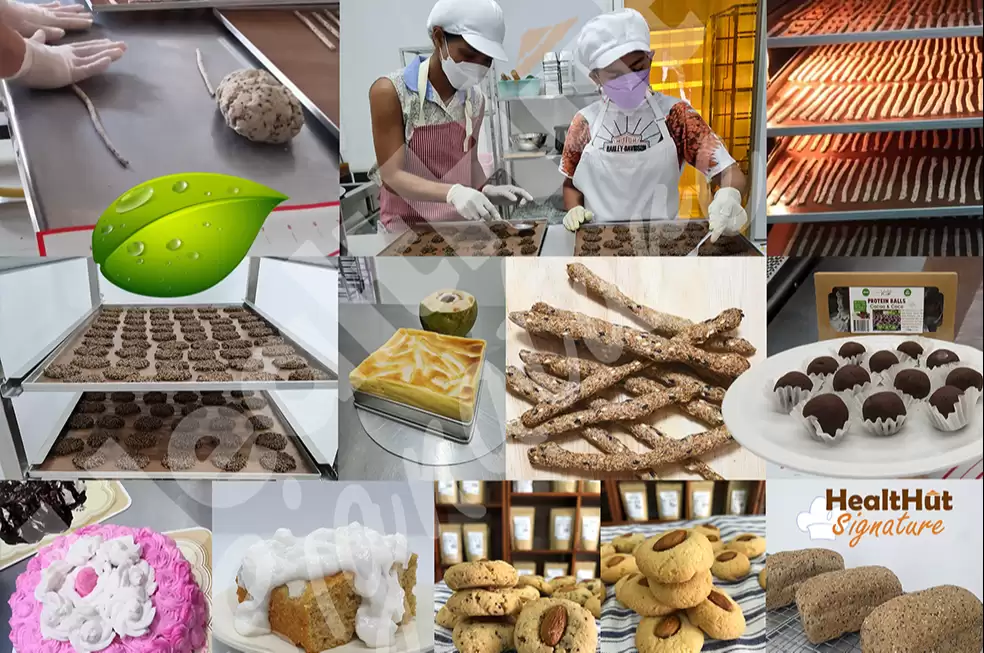

We're making safe, clean & healthy foods. Our facilities are 100% wheat flour free
Know more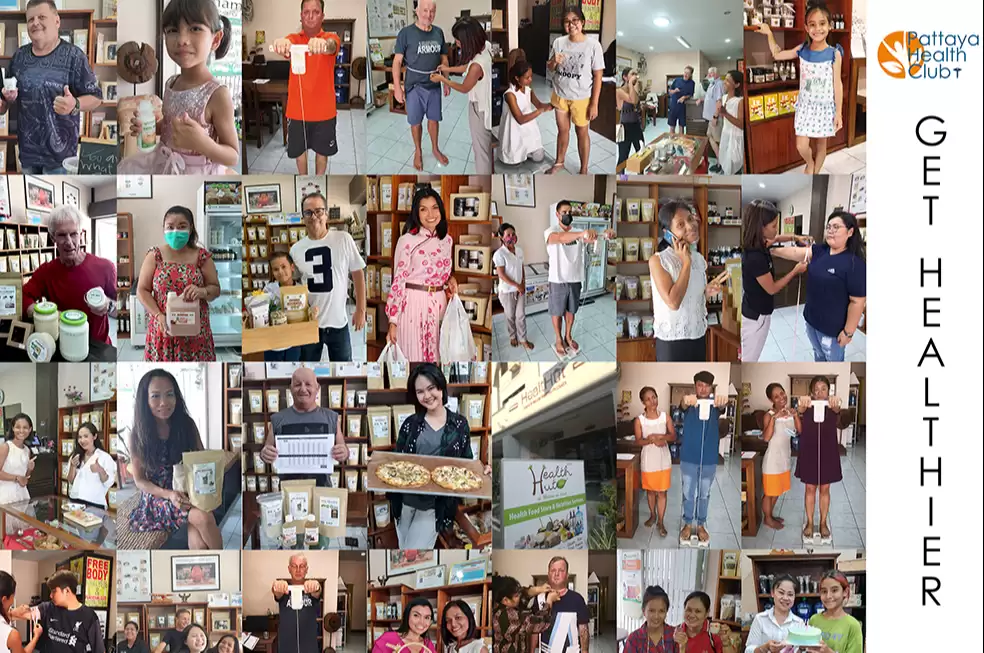
Join our Health Club and enjoy discount, free guidance, education and follow-up sessions!
Join the Club!
We understand our customers' needs for safe, clean, and healthy food, and we take the word “quality” seriously. [...]
Read more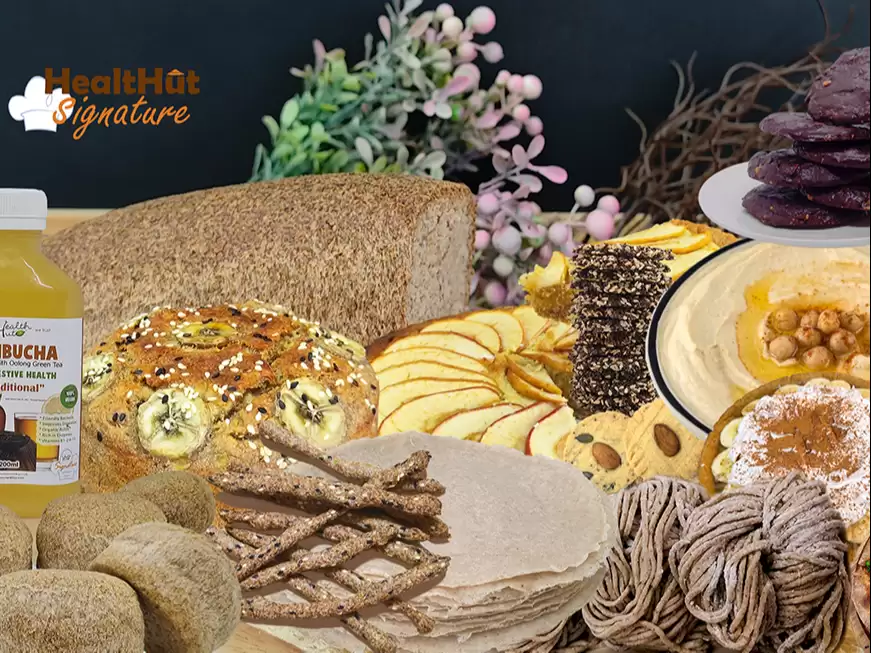
At Healthut, we have always pursued the same goal: to create the ideal foods.Foods that:Contain all the [...]
Read more
Where what you eat doesn’t just fuel your body but also plays mind games with your psyche. Here’s a bite-sized rundown: [...]
Read more